Equity dilution means change in the percentage ownership of shareholders. As the percentage ownership will change it will result in change in the profit/loss of shareholders. Let’s see this with a hypothetical example.
Assume that there is a company with 10 shares outstanding. There are only 2 shareholders both holding equal shares i.e. 5 shares each. We also assume that company earns Rs. 1000 profit.
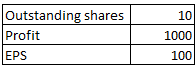
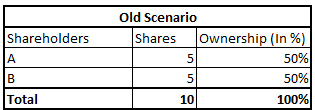
As we have assumed that company earns Rs. 1000 profit. So let’s see how the profit will be distributed among shareholders.
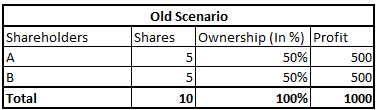
In this case, both shareholders are earning profit of Rs.500.
Now assume that company needs more capital and new 10 shares are issued by the company. Also we assume that new capital was used efficiently and Rs. 1200 was the profit generated on new capital.
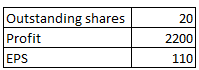
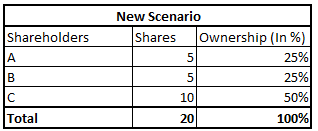
Now, let us see how the profit will be distributed.
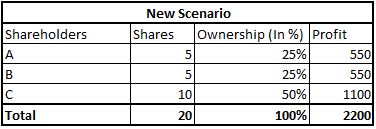
So in this case, earlier there were only 2 shareholders, both having percentage ownership of 50%. Profit was equally divided among them. But as they raised new capital,their profits also went up and their earnings increased (from Rs. 500 to Rs. 550). Hence their percentage ownership decreased but their earnings increased. This is called EPS accretion i.e. equity dilutes but EPS increases.
Hence, equity dilution may not lead to EPS dilution every time.
Wait. What is EPS Dilution? Lets take the same example again to understand it.
The case is same as above i.e. there are two shareholders having ownership of 50% each in a company. Earlier the profit was Rs. 1000 which was equally distributed among them. But they raised additional capital by issuing new shares and hence their equity was diluted.
But this time the capital was not used efficiently and company ended up earning a profit of Rs.700 on additional raised capital.
So let us see how the profit will be distributed now.
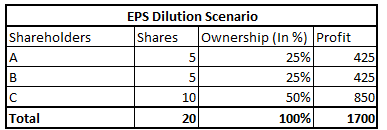
In this case, as the capital was not used efficiently, profits were lower which lead to lower earnings for both ‘A’ and ‘B’. This is called EPS dilution i.e. earnings decrease.
Hence, two ratios are important in equity dilution and EPS dilution concept. First is RoIIC i.e Return on Incremental Invested Capital. This shows the return company generate on new invested capital. And second one is high P/E. If company’s P/E is high then equity dilution can be profitable because company is getting higher amount.